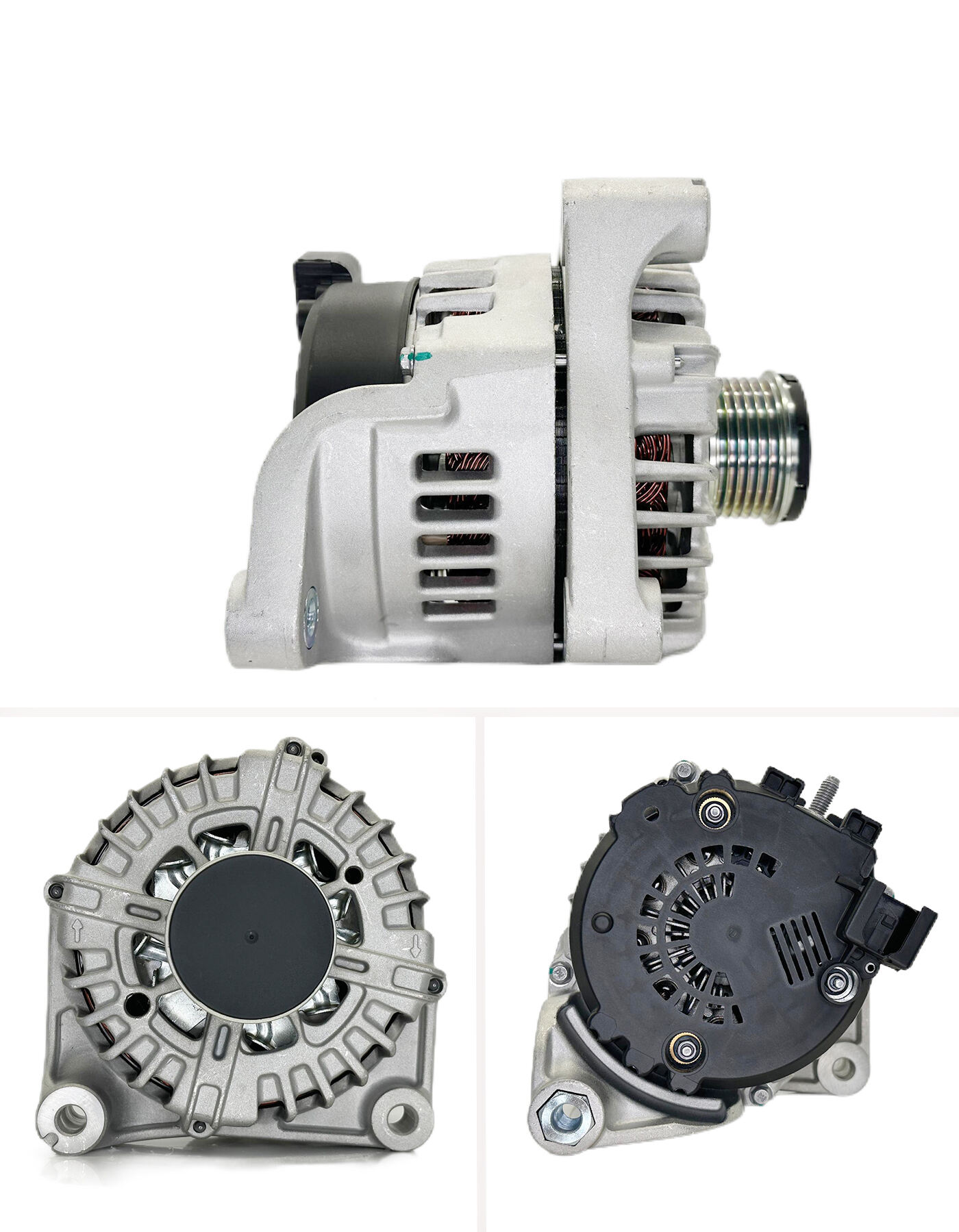
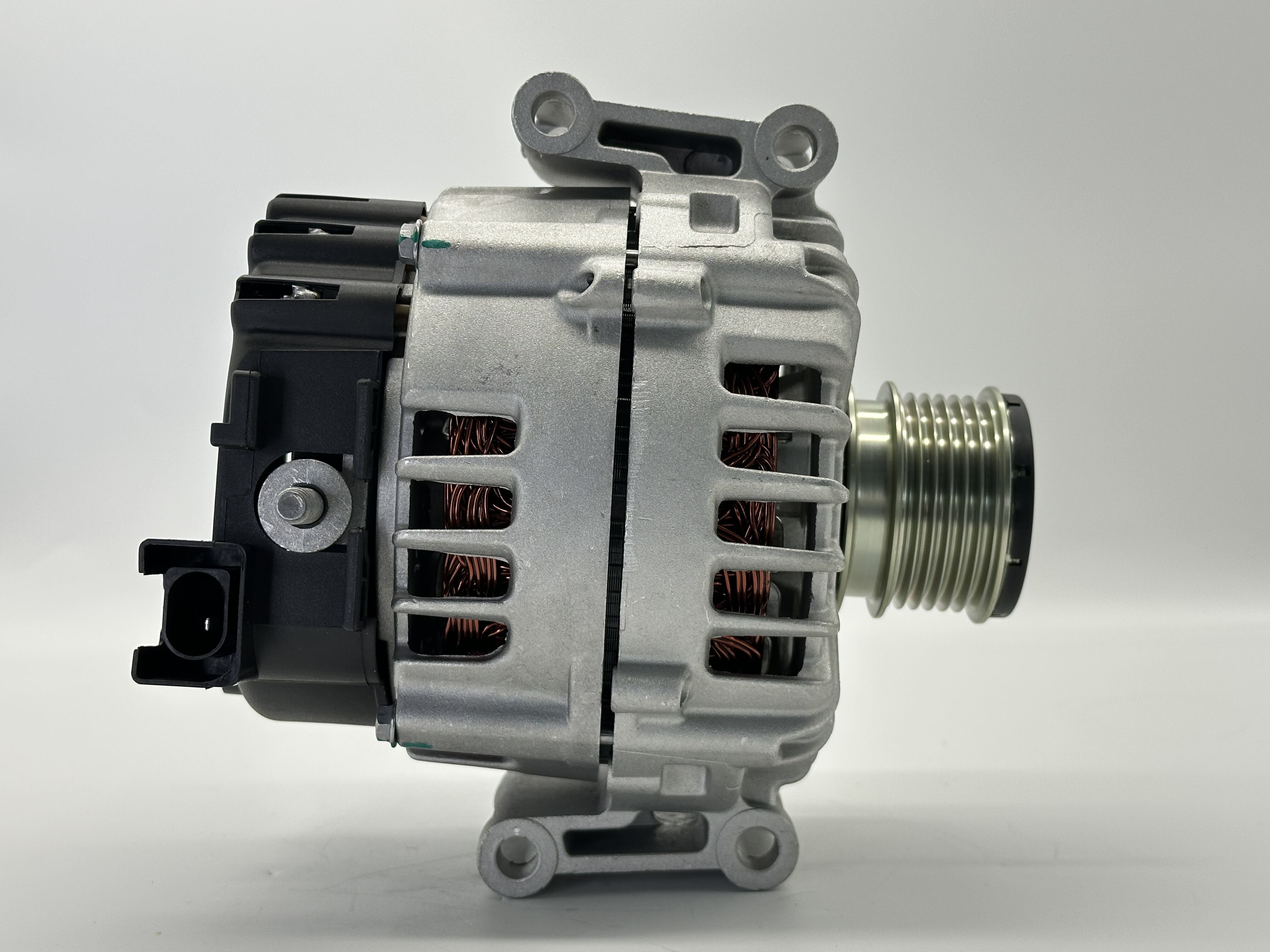
turbo alternator
A turbo alternator is a sophisticated power generation system that combines a turbine and an alternator to efficiently convert mechanical energy into electrical power. This crucial piece of equipment consists of a steam or gas turbine directly coupled to an alternator, operating at high speeds typically ranging from 1500 to 3600 RPM. The system works by utilizing the kinetic energy of steam or gas to rotate the turbine blades, which in turn drives the alternator's rotor, generating electricity through electromagnetic induction. Modern turbo alternators feature advanced cooling systems, typically using hydrogen or air, to maintain optimal operating temperatures and enhance efficiency. These machines are designed with precision-engineered components, including advanced bearing systems, excitation controls, and protective mechanisms that ensure reliable operation under varying load conditions. The capacity of turbo alternators can range from several megawatts to over 1000 MW, making them suitable for various applications from industrial power plants to large-scale utility generation. Their design incorporates sophisticated monitoring systems that continuously track parameters such as temperature, vibration, and electrical output to maintain safe and efficient operation.